Implementing the KANBAN method in its 3 forms
The Kanban method (information label in Japanese) is a visual and manual production and supply management system.
ALBERT DELOIN has developed an application method and a design of the Kanban method adapted to the majority of industrial activities. Kanban is the primary tool for applying the pull flow logic.
Take a look at our software for implementing the Kanban method.
Manual Kanban or “paper” Kanban
In addition to its effect of decreasing stock, reducing lead times and improving the service rate, the greatest merit of the Kanban method consists in a visual real-time communication of quality for all parties involved in the industrial flow, which makes it possible to:
Delegate the daily reality of production to production operators (planning, manufacturing, delivery)
Give the management the time for the tasks of the future and in particular for implementing just-in-time tools (S.M.E.D, Poka-Yoke, Total Quality, Hoshin, Kaizen, 5S, etc.)
Manual Kanban is efficient, but it has a number of drawbacks:
- Difficult to maintain beyond a certain volume of references,
- Not suitable for management between remote sites (loss of labels),
- No management of products to order or seasonal products,
- It does not provide statistical information: ADC control, deadlines, performance, etc.
- No means of estimating costs,
- Etc.




Electronic (or virtual) Kanban or e-Kanban
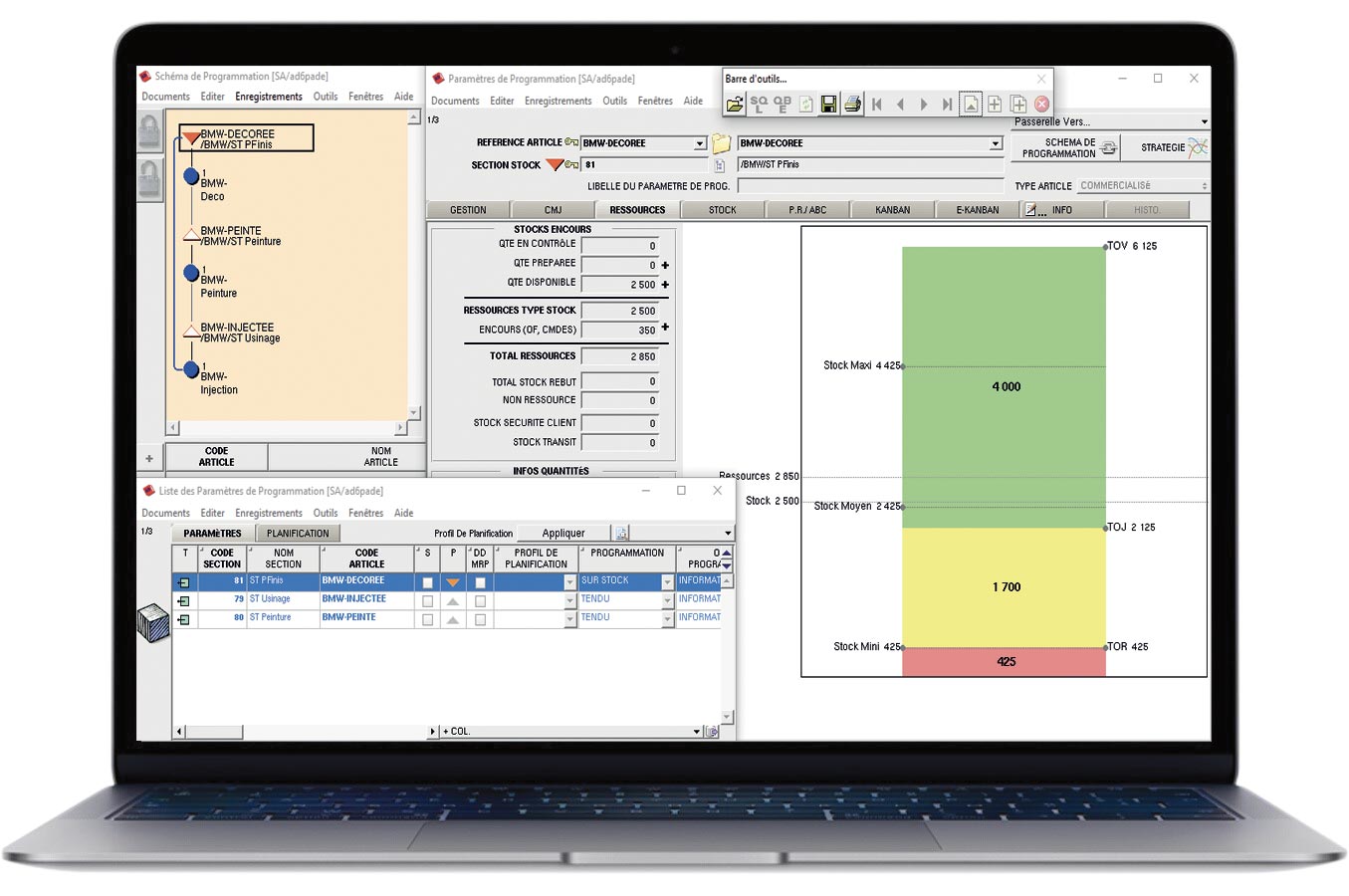
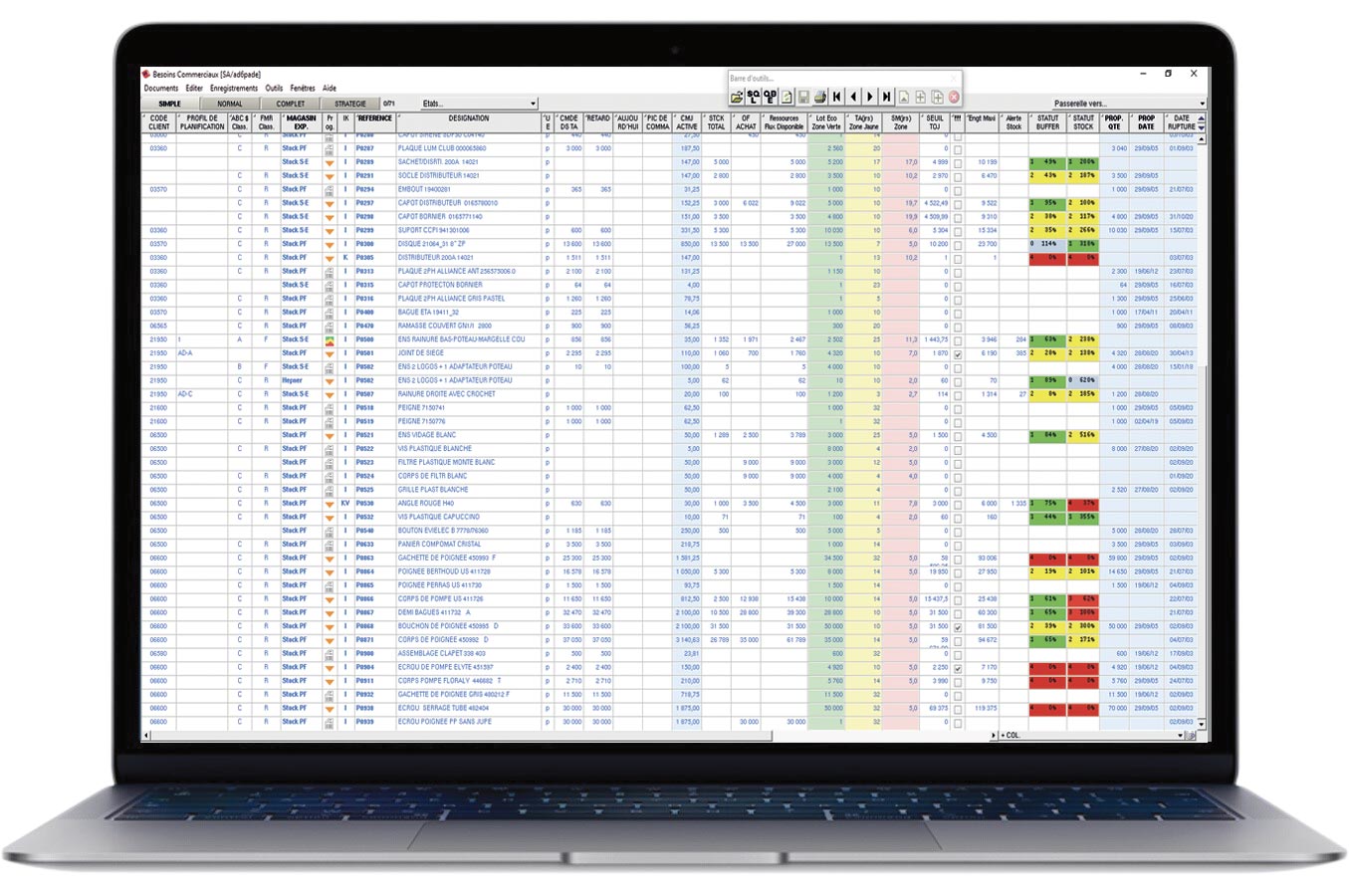
Thanks to a computerised trigger with a Kanban label printed on purpose (barcode or RFID), Kanban replaces OF. It offers all the advantages of Kanban while eliminating most of the drawbacks above if it is integrated into a complete supply chain management tool such as the AD6 software range.
Electronic Kanbans are printed at the proximity of the “producer”. They are attached (glued) to the boxes and consumed (destroyed) upon their consumption. Each of these actions is the subject of a message that tracks the life cycle of the Kanban label.
Similar to electronic Kanban, e-Kanban makes it possible to implement Kanban loops between customers and external suppliers.
IT Kanban
The rules (parameters, triggers, etc.) are similar to the traditional Kanban, but there are no labels and the schedules are replaced by computer control dashboards (see the AD6 and PFP6 software).