The DDMRP method (developed by Carol Ptak and Chad Smith, co-directors of the Demand Driven Institute) is fully integrated into our offer. Most of the basic mechanisms of the DDMRP method were already present in the PFP6 method and in the AD6 software range.
DDMRP is a method for planning and executing supply, manufacturing and distribution scenarios. It consists of implementing buffers at strategic locations in the supply chain, whose objective is to decorrelate the need (demand) from production (or supply): this is consumption
(*) The buffers are an expression of the daily consumption (ADC), lead time, launch batch and the risk of variation (security).
It is important to note that the DDMRP method is a pull flow management method:
- The 3 DDMRP buffers are an equivalent of the pull flow setting in the Kanban method,
- The trigger rule (available flow equation) is comparable to the Kanban rule, except that it incorporates demand peaks (non-standard needs).
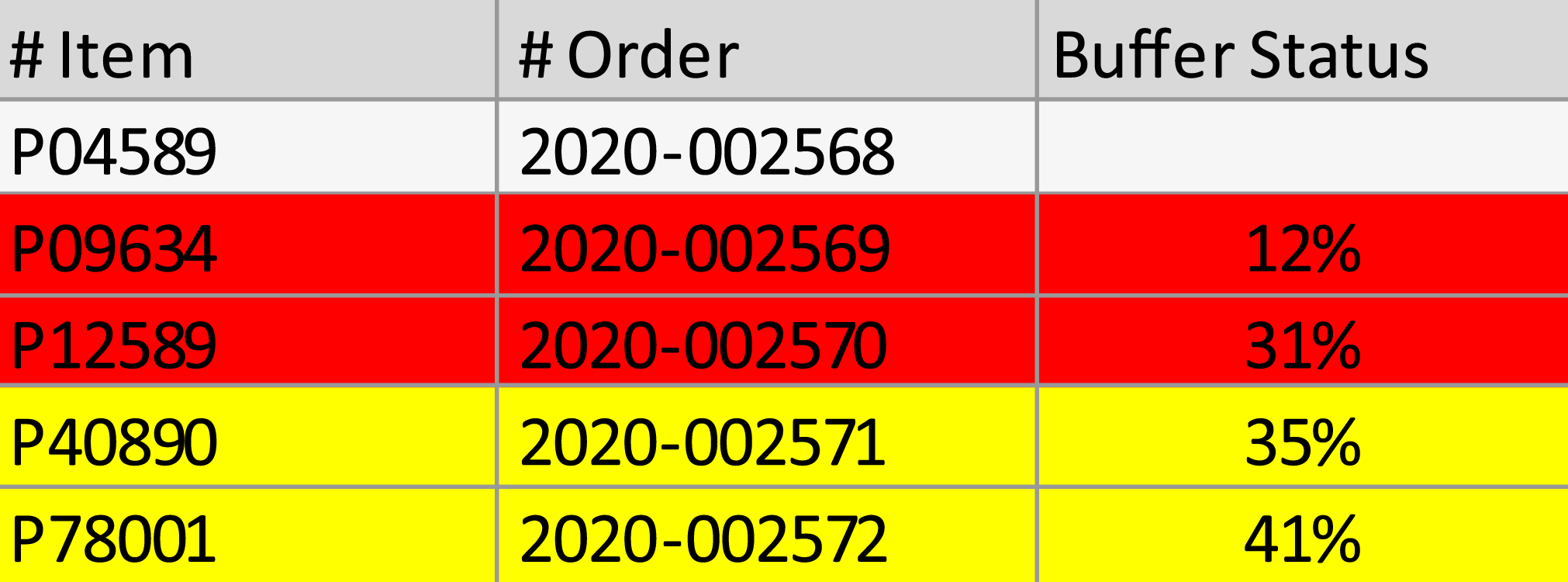
Positioning of buffers
Strategic decouplin
Buffers
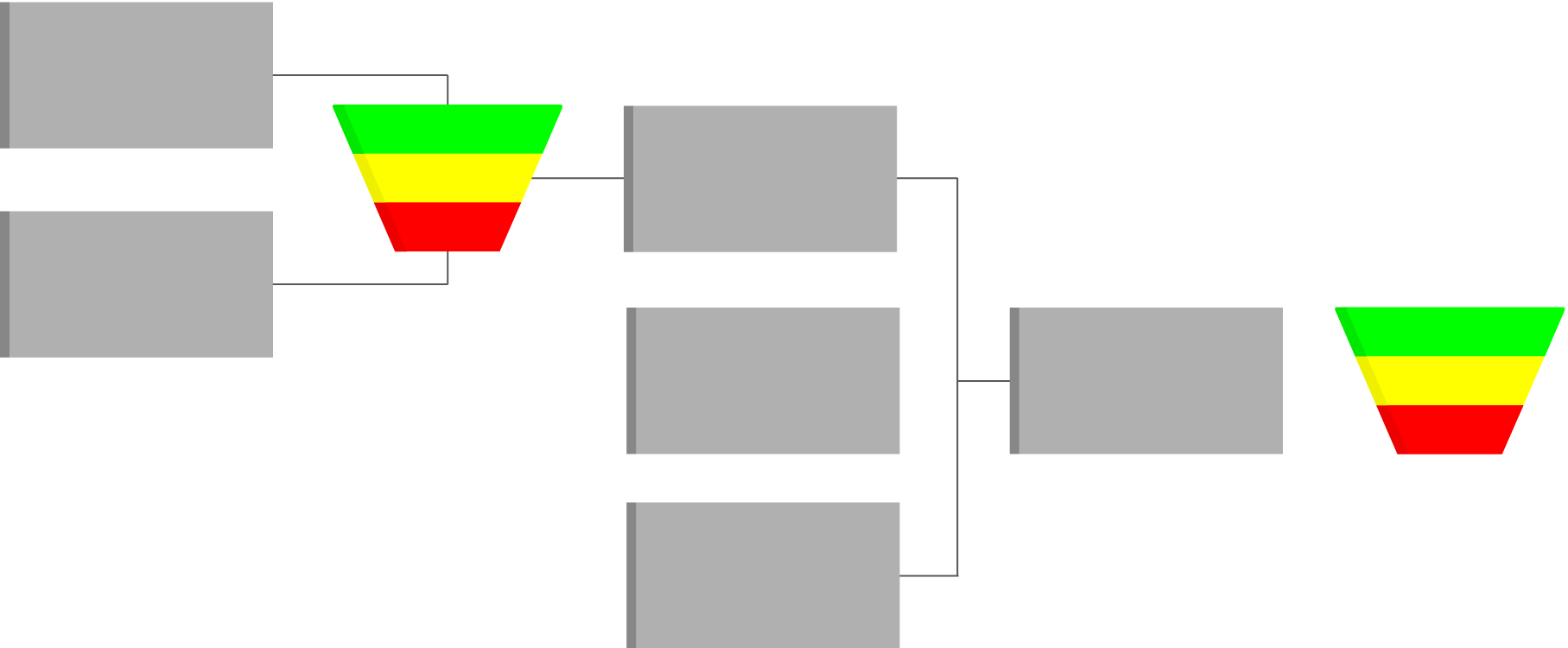
Defining profiles and calculating levels
Buffers
Dynamic adjustment according to demande
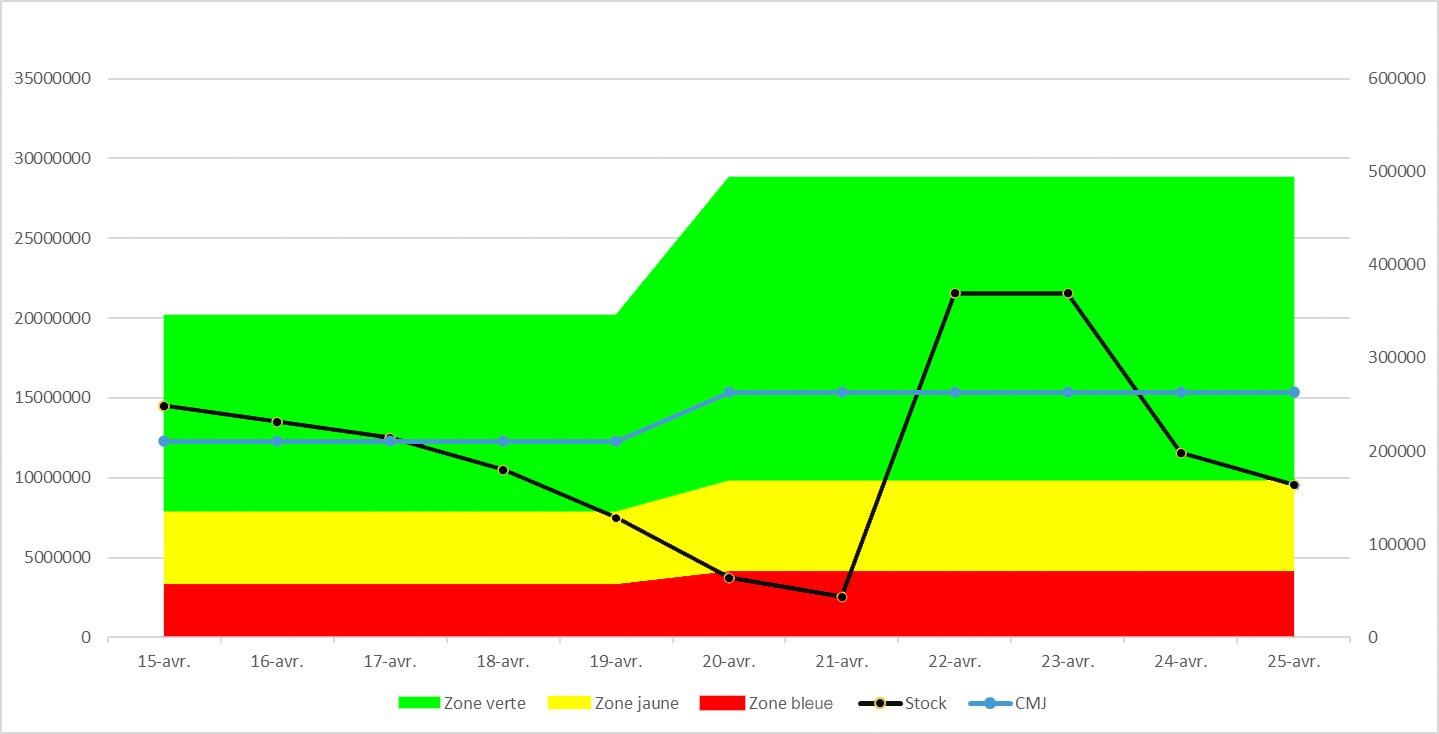
Planning
Demand-driven planning
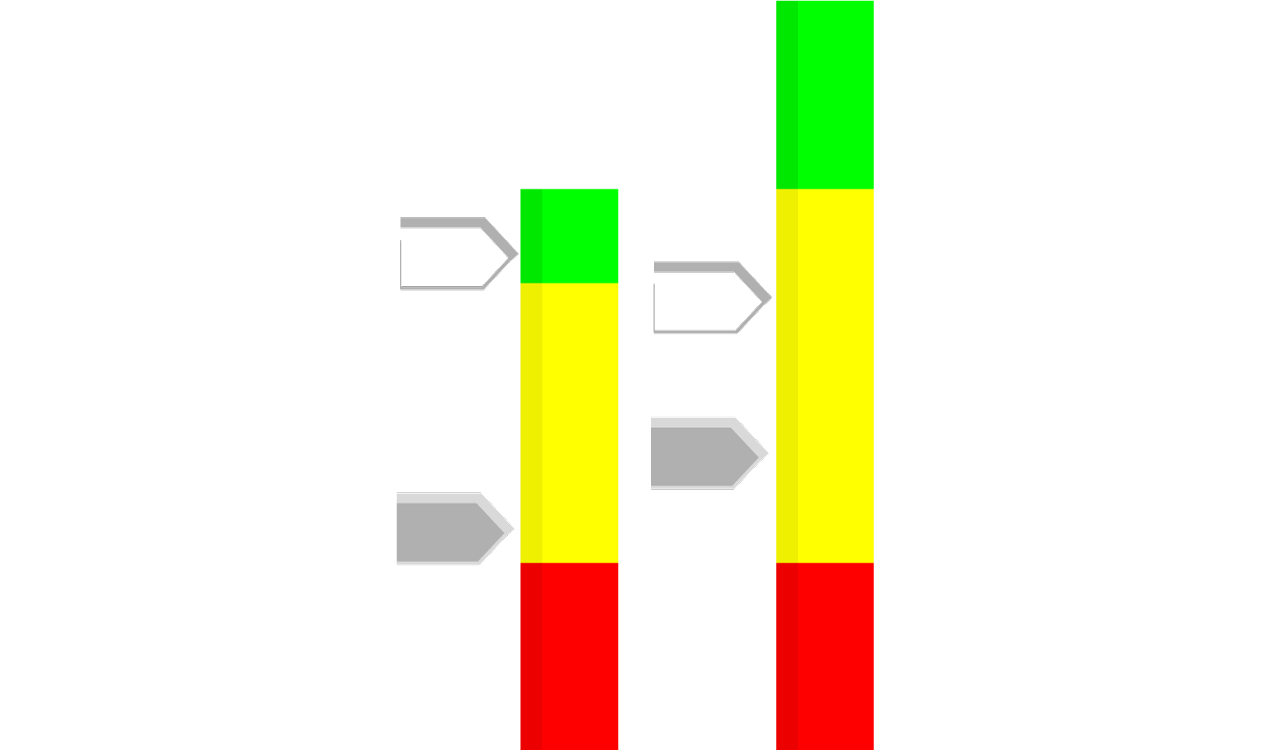
Execution
Visual and collaborative execution